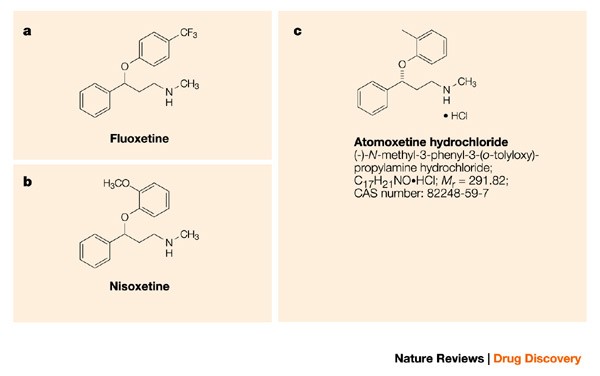
Atomoxetine and circadian gene expression in human dermal fibroblasts from study participants with a diagnosis of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder | SpringerLink
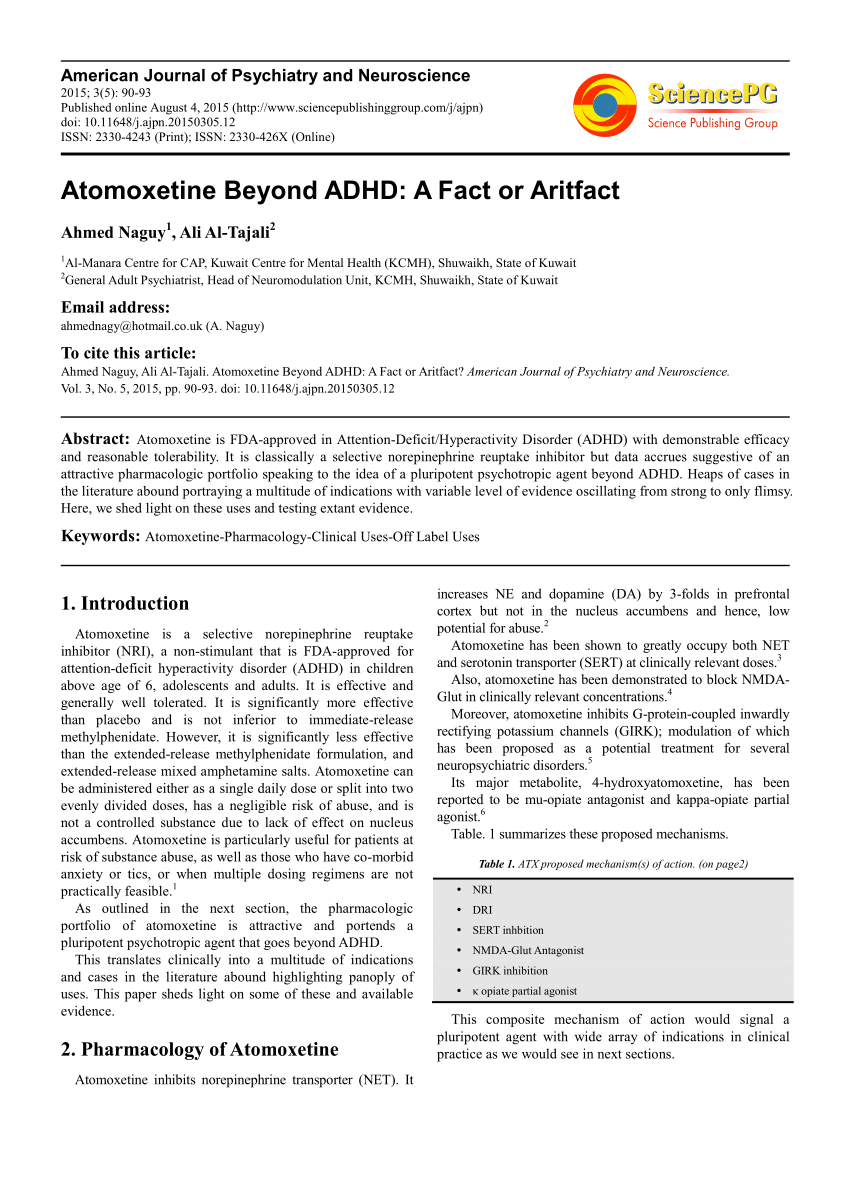
Atomoxetine and circadian gene expression in human dermal fibroblasts from study participants with a diagnosis of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder | SpringerLink

Alternations in nuclear factor kappa beta activity (NF-kB) in the rat brain due to long-term use of atomoxetine for treating ADHD: In vivo and in silico studies - ScienceDirect
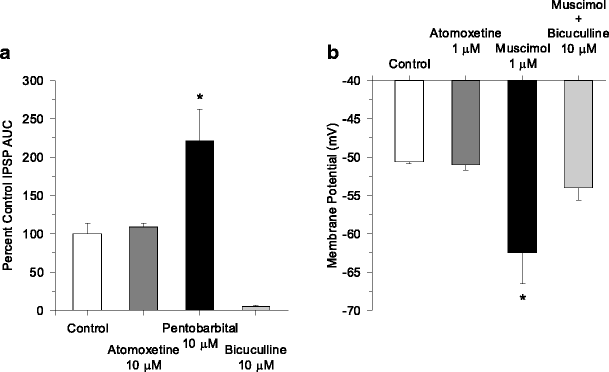
A review of the abuse potential assessment of atomoxetine: a nonstimulant medication for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | SpringerLink

Studying Medicine on Twitter: "#Alkaloids in #opioids act (agonists) on human #brain natural “mu-opioid” #receptors; Antagonist: naloxone, partial agonist: buprenorphine https://t.co/DC3sZJxH2f" / Twitter
Atomoxetine, ADHD, and the ongoing debate about increased risk of suicidal behaviors: the understudied role of kappa opioid rece
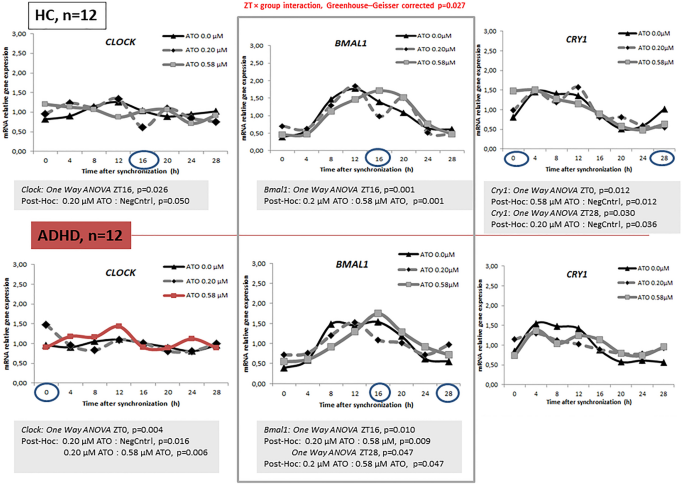
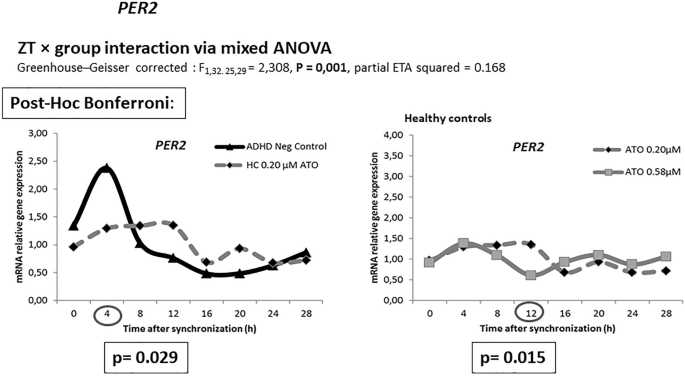
Atomoxetine and circadian gene expression in human dermal fibroblasts from study participants with a diagnosis of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder | SpringerLink

Methylphenidate and Atomoxetine Inhibit Social Play Behavior through Prefrontal and Subcortical Limbic Mechanisms in Rats | Journal of Neuroscience

Behavioral effects of the kappa opioid receptor partial agonist nalmefene in tests relevant to depression - ScienceDirect

Kappa Opioid Receptor Ligands and Pharmacology: Diphenethylamines, a Class of Structurally Distinct, Selective Kappa Opioid Ligands | SpringerLink

Synthesis and biological evaluation of the major metabolite of atomoxetine: elucidation of a partial κ-opioid agonist effect - ScienceDirect

Mixed Kappa/Mu Partial Opioid Agonists as Potential Treatments for Cocaine Dependence - ScienceDirect
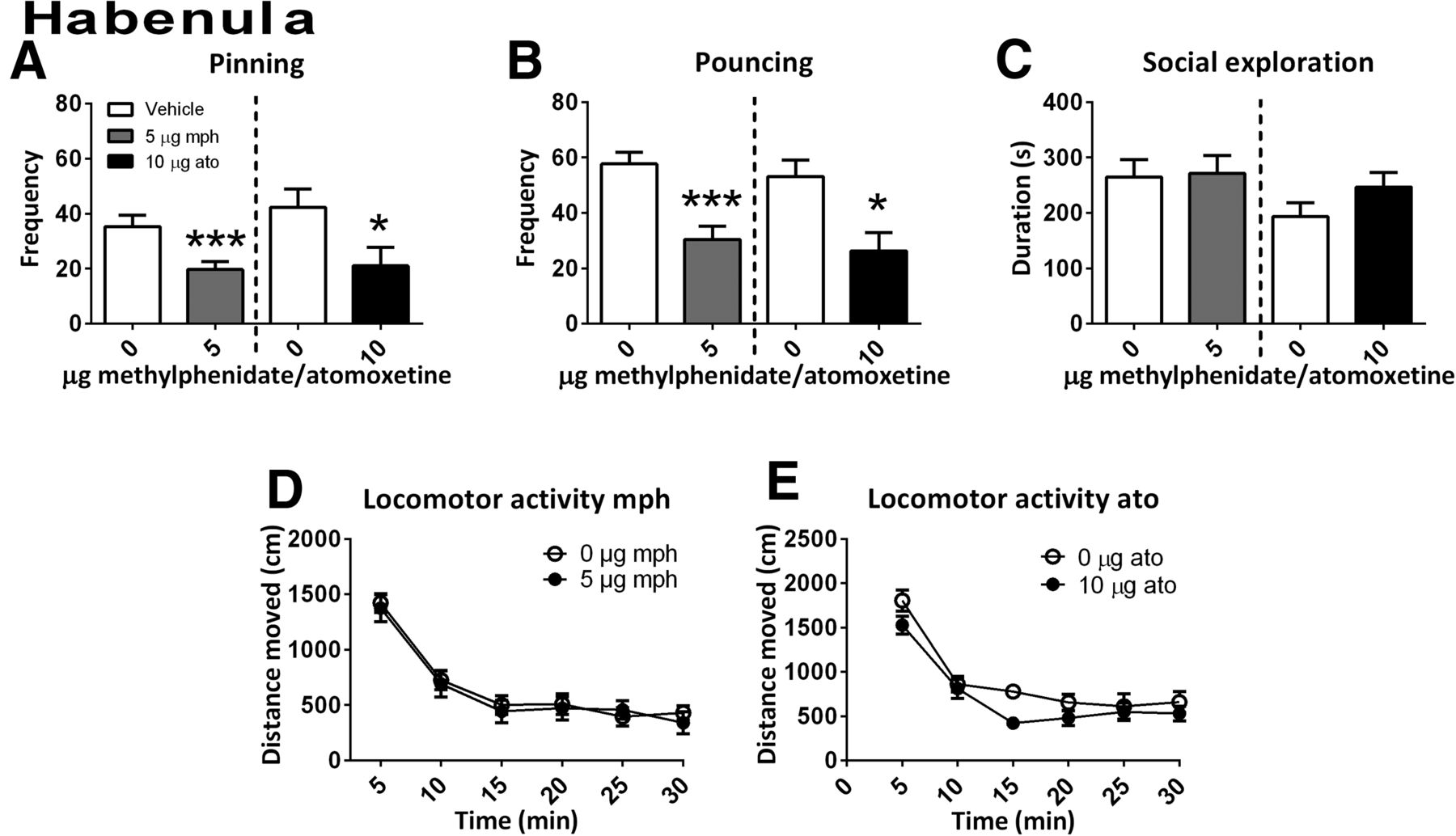
Methylphenidate and Atomoxetine Inhibit Social Play Behavior through Prefrontal and Subcortical Limbic Mechanisms in Rats | Journal of Neuroscience

Synthesis and biological evaluation of the major metabolite of atomoxetine: elucidation of a partial κ-opioid agonist effect - ScienceDirect
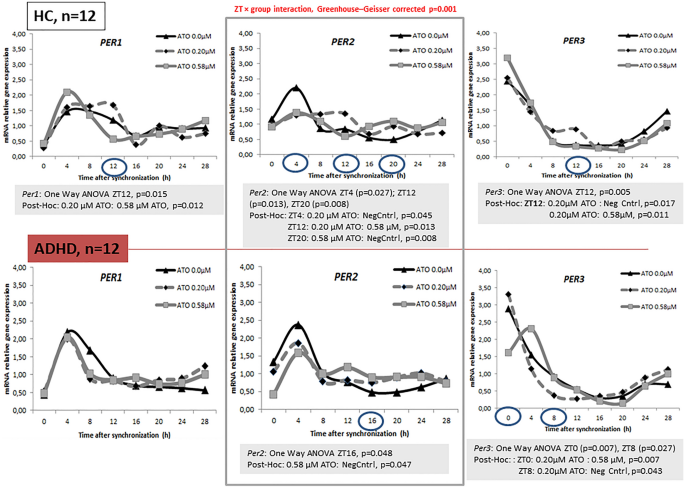
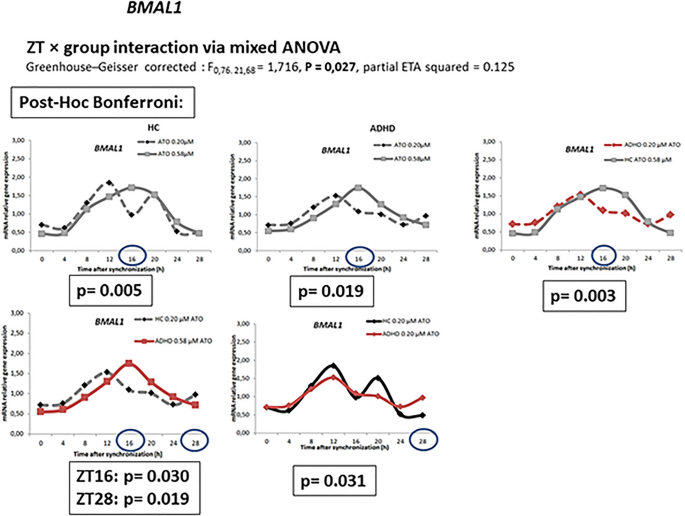
Atomoxetine and circadian gene expression in human dermal fibroblasts from study participants with a diagnosis of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder | SpringerLink

Synthesis and biological evaluation of the major metabolite of atomoxetine: elucidation of a partial κ-opioid agonist effect - ScienceDirect
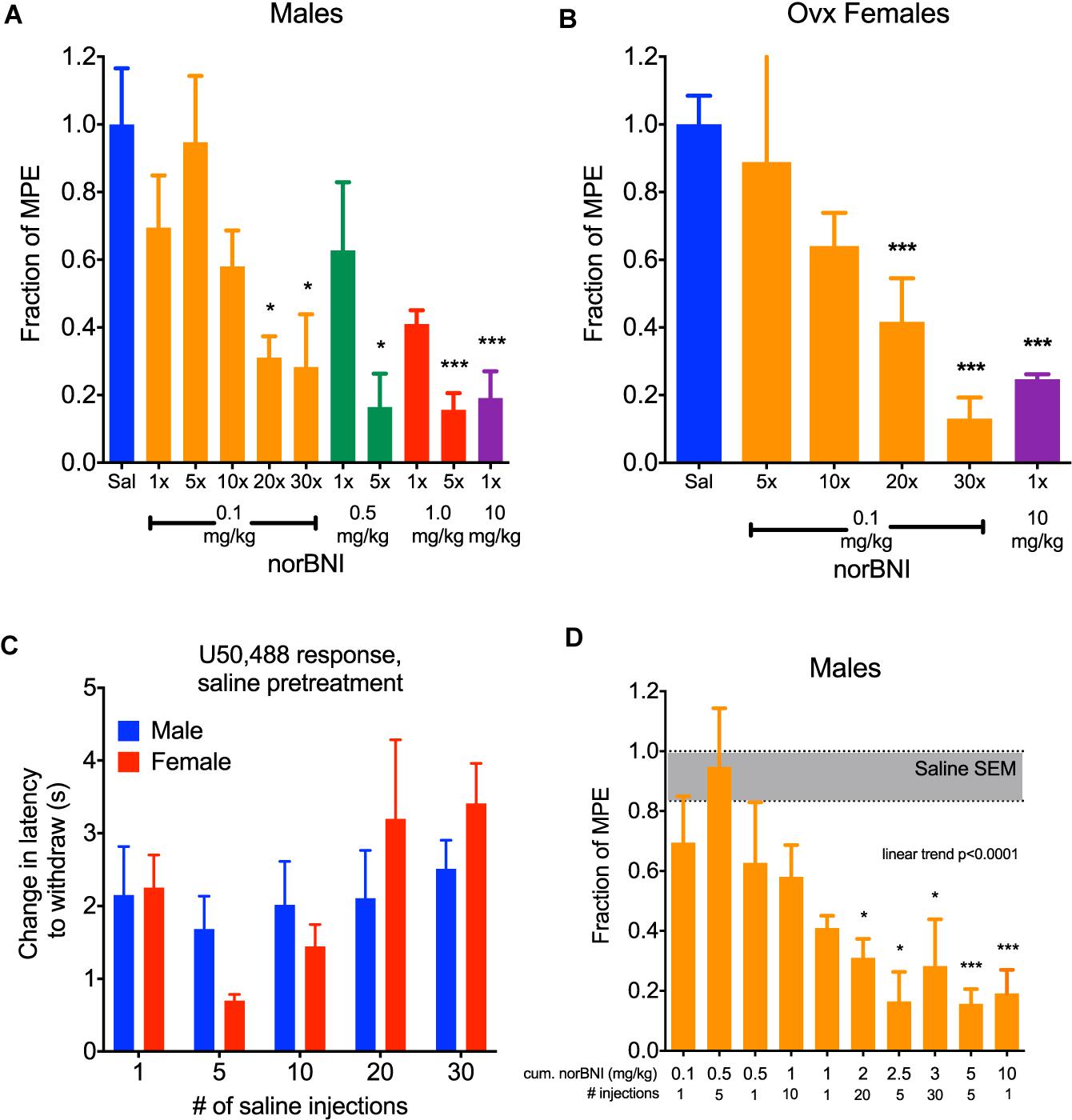
Frontiers | Repeated Administration of Norbinaltorphimine Produces Cumulative Kappa Opioid Receptor Inactivation

Methylphenidate and Atomoxetine Inhibit Social Play Behavior through Prefrontal and Subcortical Limbic Mechanisms in Rats | Journal of Neuroscience